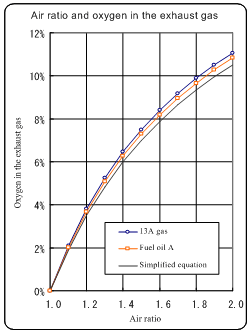
* The simplified equation for
obtaining the
air ratio is:
Air ratio = 21/(21 - O2% value)
where O2 is the oxygen content obtained by
analysis (dray base value).
* Normally, the air ratio may
be calculated
by this equation. The criteria
of the Law
Concerning Rational Use of Energy
specify
this equation.
* As the air ratio becomes large,
the difference
between the result obtained by
the simplified
equation and the real value becomes
large.
(See the graph.)
* The air ratio is defined as
"real
air value/theoretical air volume."
*The air ratio of 1 (one) represents
an ideal
state in which no more than required
air
is used for combustion (theoretical
combustion).
*The air in excess of air ratio
at 1 (one)
is called "excess air"
which causes
heat loss by carrying out air
from the stack
at heated state.
* The air ratio short of 1 (one) causes incomplete
combustion, associated with the incomplete
combustion heat loss.
|
 |
|