Water Tube Boiler
| AEEC Home | Training Index | Index | Top | Previous | Next |
| ECCJ / Text for Training Courses | Thailand |
3) Characteristics for Each Method |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2. Application Examples to Industrial Field |
2. Application Examples to Industrial Field |
|
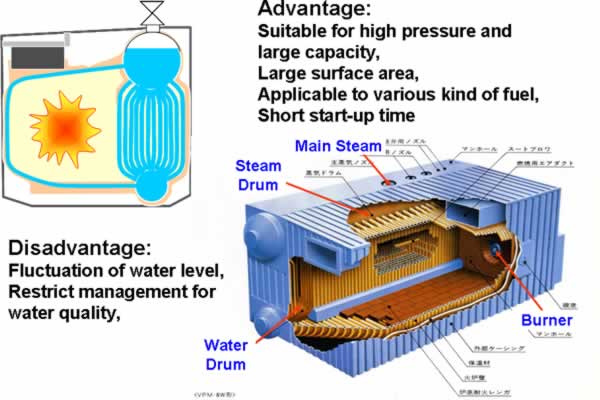
1) Boilers Heat up water to generate steam or hot water which utilize for process heat, air conditioning, chemical processes, etc. Category (1) Water tube boilers (2) Fire tube boilers (3) Small One-through boilers Number of Annual Installations : Approx. 15,000 Units/Year (1990-2000) |
Water Tube Boiler |
 |
|
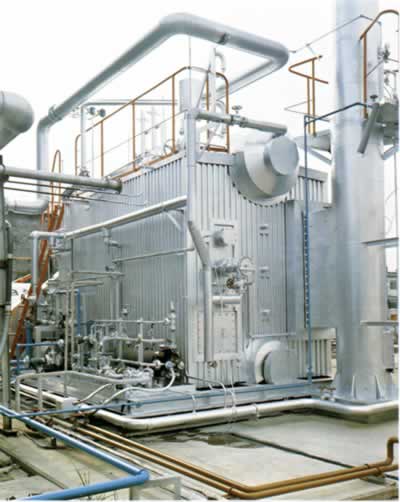
Water Tube Boiler
|
 |
| 3/23 Next |
| AEEC Home | Training Index | Index | Top | Previous | Next |