What is energy conservation?
1. Minimization of energy loss(prevention and recovery)
2. Maximization of energy usage efficiency

| AEEC Home | Training Index | Index | Top | Previous | Next |
| ECCJ / AOTS Malaysia training course | Malaysia |
|
2. Practice of Energy ConservationActivities
in Japanese Enterprises
|
|
What is energy conservation?
|
| lamp"rational use of energy" the
Energy Conservation Law 1. Minimization of energy loss(prevention and recovery) 2. Maximization of energy usage efficiency |
 |
| < "energy management"is the
baseof energy conservation > "Energy Management"procedure |
| Energy Managementmeans the total execution of fact-finding, planning, improvement and evaluation to get the cost-down profit. |
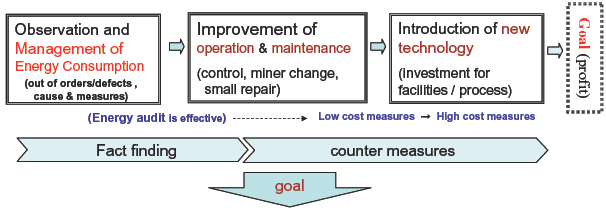 |
| Operation improvement, Technical improvement Cost reduction, Strengthening international-competitiveness Key point: propelling-organization and key person (top management and energy manager) |
| Three Steps to Promotion of Energy ConservationThree Steps to Promotion of Energy Conservation | ||||||||||||
|
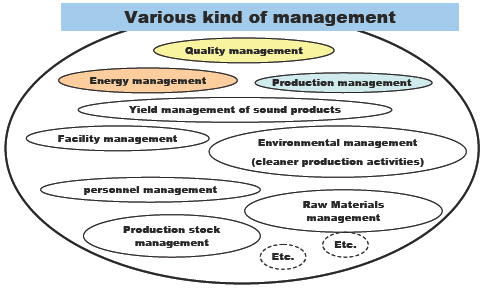
| "Management"is one of the most important activities inenterprises for Profit Maximization."Energy management"is one element of Cost management | |
 |
|
|
|
|
| Concrete items should be managed |
| the energy conservation lawshows concrete
items for energy management as the judgment
standards and management standards. < guide line > |
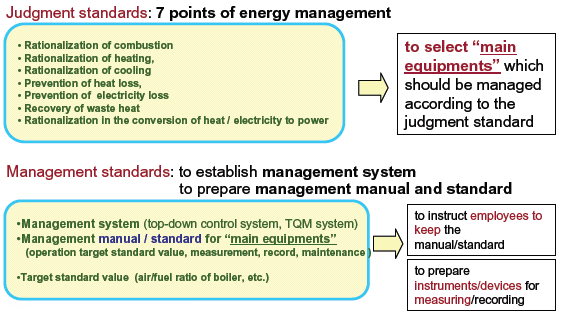 |
| Energy management starts from Operation Management |
| 1.Operational Condition Management *to keep the operational standard. *to find the trouble in operation (or with a machine). *to prevent energy waste(keep the standard, operational/technicalimprovement). 2.Operational ResultManagement <energy consumption/ unit consumption management,yield management, etc.> *to reduce energy consumption and energy cost (technical improvement, introducing high efficiency facilities, etc ). *Both kinds of management are necessary for energy conservation. *Especially the latter is indispensable for top management. |
| 3/14 Next |
| AEEC Home | Training Index | Index | Top | Previous | Next |
|
Copyright(C) ECCJ 1996-2019
|