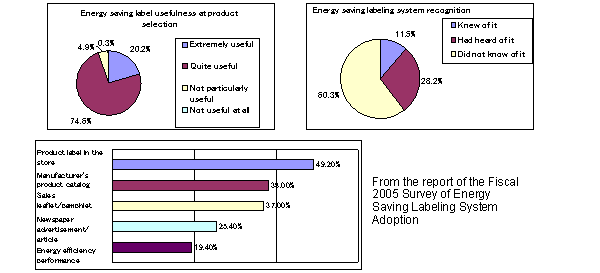
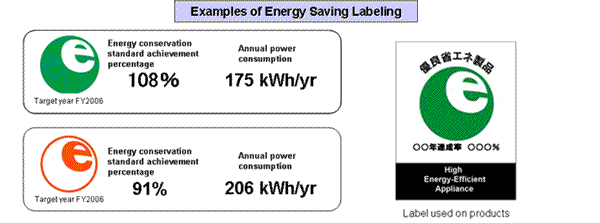
The importance of the roles played by retailers of
household appliances, etc.
household appliances, etc.
- If energy-efficient products are manufactured, there will be no energy savings benefits if consumers do not purchase those products.
- Consumer awareness of energy conservation issues is increasing, and the dissemination of accurate energy conservation information is essential to the widespread adoption of energy-efficient products. (Energy-conscious consumers account for a very high 93.3% of the total number.)
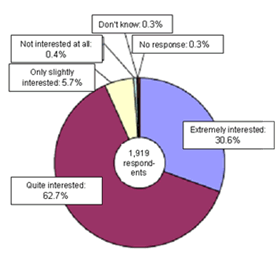
Source: FY1995 Nation Life Monitor Findings