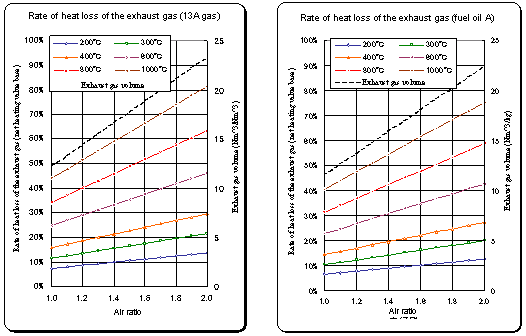
Larger air ratio leads to larger heat loss
with the exhaust gas.
| AEEC Home | Training Index | Index | Top | Previous | Next |
| ECCJ / AOTS Malaysia training course | Malaysia |
|
Larger air ratio leads to larger heat loss
with the exhaust gas.
|
 |
|
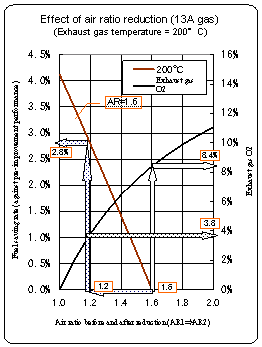
Fuel saving by air ratio improvement
|
|
| Reduction of the air ratio (reduction of
O2% in the exhaust gas) reduces heat loss
with the exhaust gas. This in turn leads to fuel saving. The graph illustrates result of air ratio reduction. In fuel saving rate, 13A gas and fuel oil A differ only very little. At lower exhaust gas temperatures, the effect is small. (Example) If air ratio can be reduced from the present 1.6 (O2 = 8.4%) to 1.2 (O2 = 3%), a fuel saving of 2.8% is realizable. |
 |
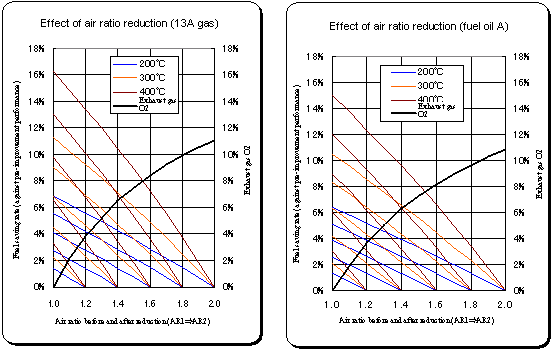
| Effect of air ratio reduction |
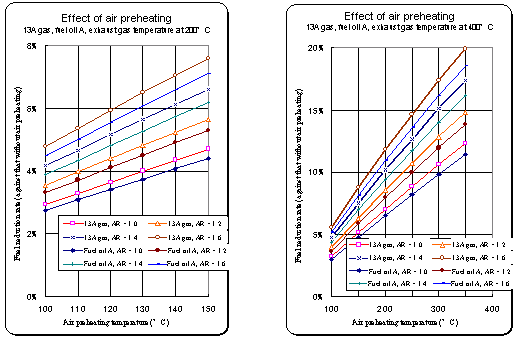
| The graphs are developed on the assumption that a change in air ratio does not affect the exhaust gas temperature. |
 |
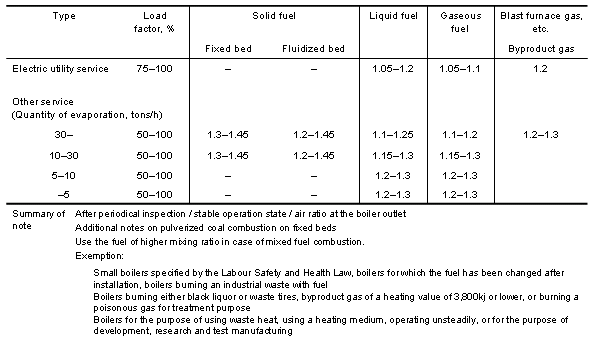
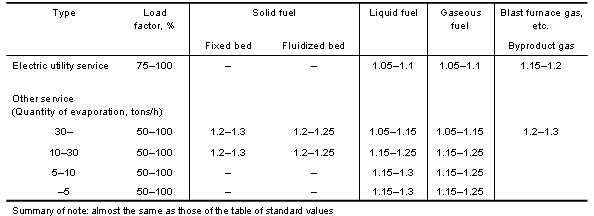
| Criteria for air ratio (standard values) (the Law Concerning Rational Use of Energy) |
| Standard air ratio for boiler |
 |
| Criteria for air ratio (target value) (the Law Concerning Rational Use of Energy) |
| Target air ratio for boiler |
 |
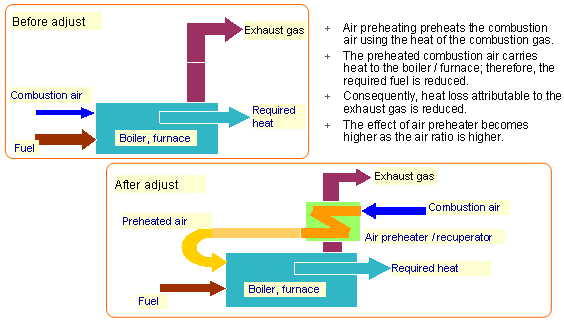
| Energy conservation by air preheating | |
 |
| Effect of air preheating |
| If the heat contained in the exhaust gas is recovered by installing an air preheater, the temperature of the exhaust gas is lowered and the required fuel is reduced. |
 |
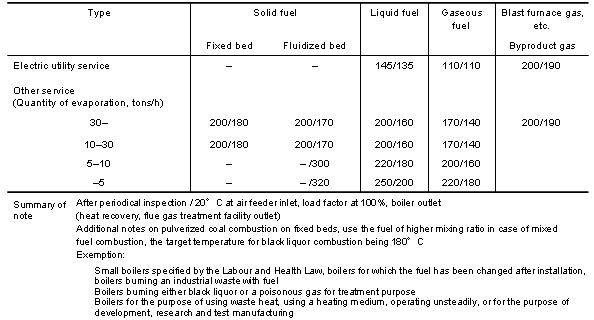
| Criteria for exhaust gas temperature (the Law Concerning Rational Use of Energy) |
| Criteria for boilers, standard / target exhaust
gas temperature |
 |
| Criteria for factories (The Energy Conservation Law) |
| The "criterion" should be observed
to the extent economically and technically
possible. The "target" is the objective to pursue to achieve a reduction of energy unit consumption of 1 (one) percent per year (average). Subjects of criteria (matters concerning standards) 1. Rationalization of fuel combustion. 2. Rationalization of heating, cooling and heat transfer. 3. Prevention of heat loss by radiation, conduction, etc. 4. Recovery of waste heat. 5. Rationalization of heat conversion into power, etc. 6. Prevention of electricity loss by resistance, etc. 7. Rationalization of conversion of electricity into power, heat, etc. Quantitatively specified item of criteria (standard value, target value) 1. Air ratio for boilers 2. Air ratio for industrial furnaces 3. Outer wall temperature of industrial furnaces 4. Exhaust gas temperature for boilers 5. Waste heat recovery rate of industrial furnaces 6. Facility for which power factor should be improved 7. Target efficiency of high-efficient totally-enclosed electric motors (02 to 37kw) |
| 3/6 Next |
| AEEC Home | Training Index | Index | Top | Previous | Next |
|
Copyright(C) ECCJ 1996-2019
|