|
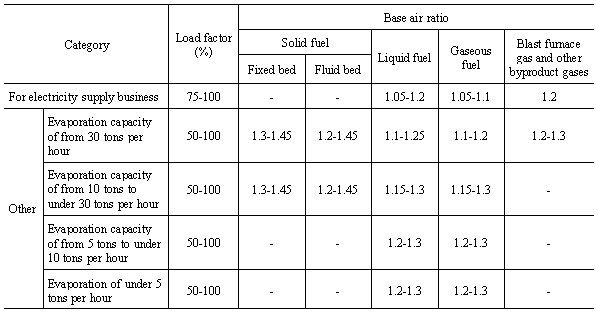
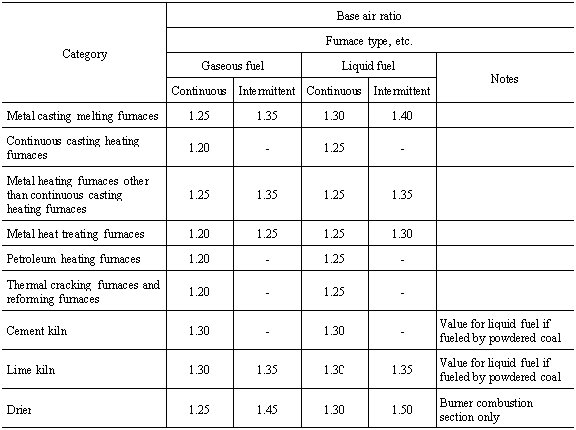
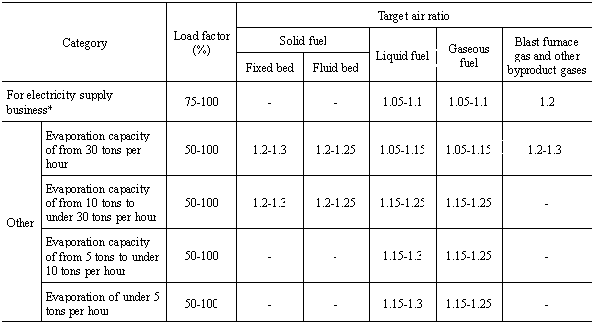
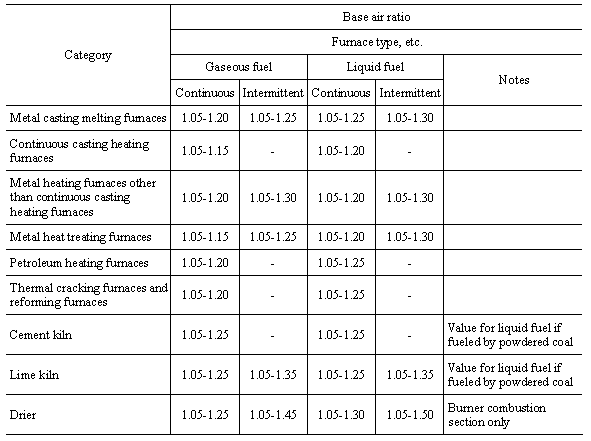
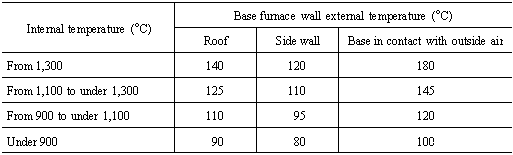
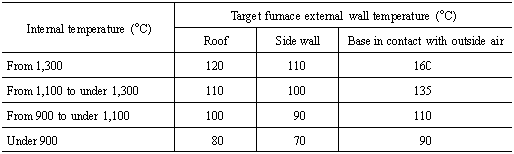
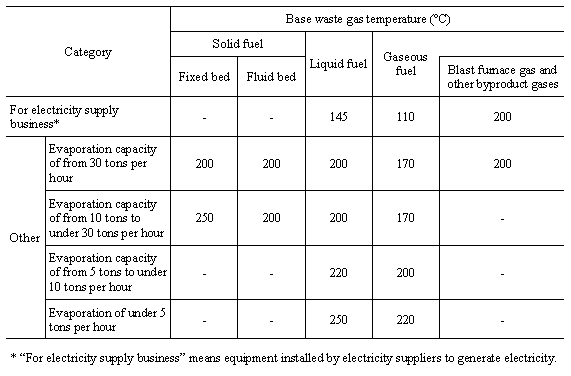
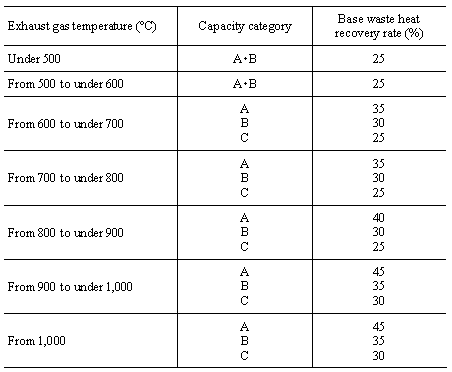
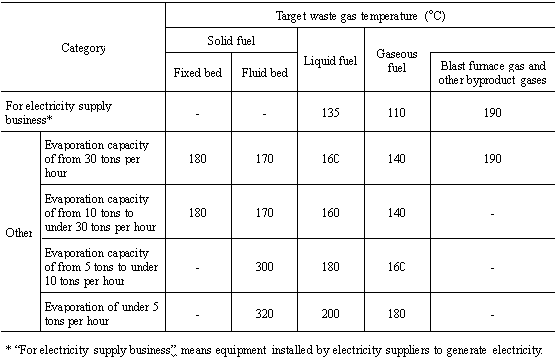
The values for target waste gas temperature given in the table
shall not apply to the waste gas temperatures of the following boilers:
(1) Small boilers provided for by Article 1.4 of the Occupational
Safety and Health Law Enforcement Ordinance
(2) Multi-fuel boilers combusting wood waste, tree bark, sludge
and other industrial waste with fuel
(3) Boilers processing toxic gas
(4) Boilers using waste heat or remaining heat
(5) Boilers not in operation at the time of periodic inspection
or otherwise not in regular operation, and boilers used for development,
research or trial production
|