- Existing problem
- Local exhaust air is expelled to the outside without heat recovery, wasting air conditioner energy.
- Improvement
- Install a full heat exchanger to exchange the heat between the local exhaust and the outside air intake to recover the exhaust heat.
- Advantage
Fuel reduction amount = 1,080kL/year x 40% x 42% = 181kL (¥5,430,000/year)
When:
- Out of the kerosene used for the boiler, the portion for air conditioning = 1,538kL x 70% = 1,080kL/year
- Local exhaust loss = 40% of air conditioning energy
- Waste heat recovery rate using full heat exchange = 42%
Reference
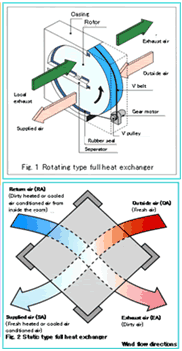
- Principle of rotating type structure
- Taking an example of cool air conditioning, when the high temperature, high humidity outside air passes through the rotor, it has its heat and humidity absorbed by the rotor. Due to the rotation of the rotor, the air will pass into the exhaust duct. Here, because the cool air conditioned exhaust air will have low temperature and humidity, the outside air will emit its heat and humidity. (Fig. 1)
- As the rotor rotates further, the exhaust air will once again absorb heat and humidity as it passes into the outside air duct, and the effect will be repeated.
- The structure consists of a laminated honeycomb structure rotor made from craft paper, etc., together with the motor driving it, and the casing.
- A large amount of desiccant (lithium chloride, etc.) is incorporated in the rotor for exchanging the humidity, and the rotor is driven by a motor that rotates approximately 8 times each minute. The heat and moisture are stored in the desiccant, and then released.
- Static type full heat exchanger
- In the static type, the heat and moisture pass through the heat exchange element.
|
 |
|