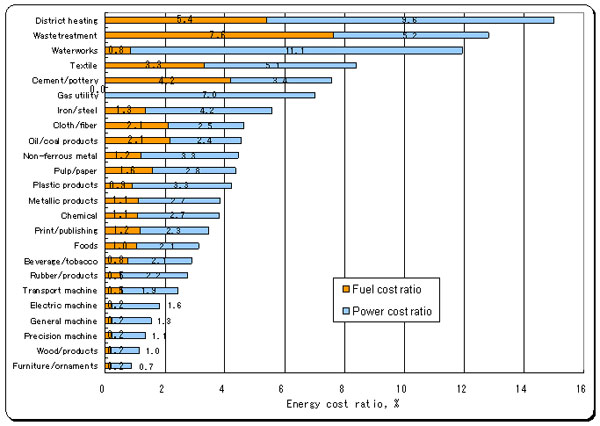
1-7.Energy cost ratio by industry type
| AEEC Home | Training Index | Index | Top | Previous | Next |
| ECCJ / TextReport | Vietnam |
1-7.Energy cost ratio by industry type |
 |
| Energy Conservation Guidebook for Factories, 2006.3 |
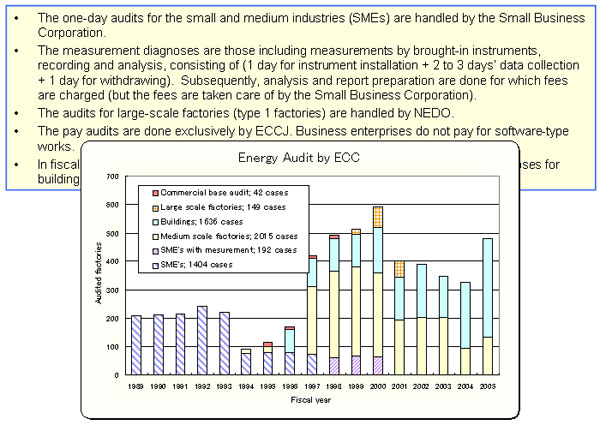
1-8.Number of audits |
 |
2. Energy Conservation Technology – combustion control and heat insulation |
|
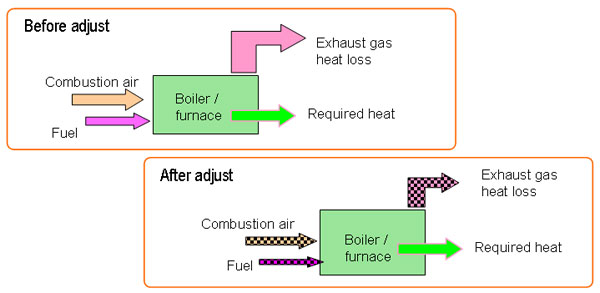
2-1.Optimization of air ratio |
|
 |
| 4/13 Next |
| AEEC Home | Training Index | Index | Top | Previous | Next |